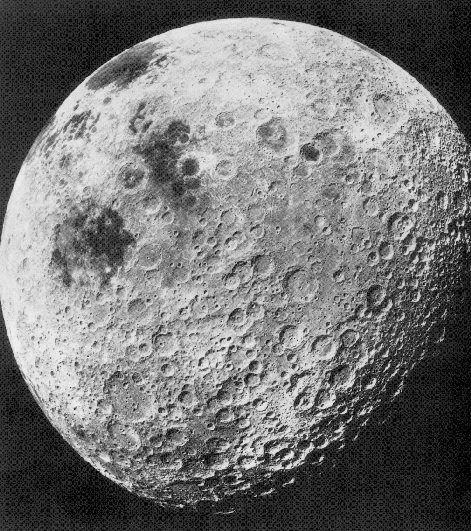
The Near Side
(at
full Moon)

The Far Side
(from
Apollo 16)
Lunar Phases: changing orientation between the Earth, Moon, and Sun as the Moon moves on its orbit.
What does the Moon look like? The Rotating Moon
The Near Side
(at
full Moon)

The Far Side
(from
Apollo 16)

Craters:
The Lunar MariaOver time, the volcanic theory died and we now recognize the lunar craters to be impact sites. Does this mean there is no evidence of volcanic activity on the Moon? No! The maria are volcanic in origin.
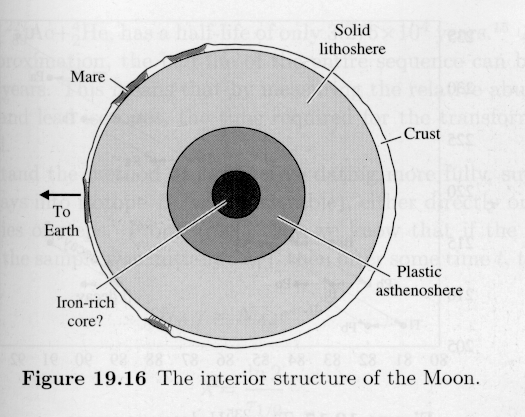
| The Moon has a thick, solid
lithosphere (unlike
the Earth), and therefore has no plate tectonics -- no
surface activity.
Many silicates are found in the Moon's crust -- composition similar to that in the Earth's mantle. In the crust, many refractory elements (high melting points) and few volatile elements (low melting points) are found, suggesting the Moon's surface was originally very hot. The volatile elements ``boiled off.'' The inner portions of the Moon are somewhat denser then the crust, but any iron-rich core must be very small. Why is the moon solid, while the Earth has a molten interior? |
 |
Cooling Time of a planet:
Rough consideration: The amount of heat production in a planet is proportional to its volume (ie more radioactive material, or more mass, etc):
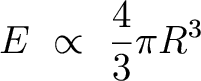
The rate at which it looses heat is proportional to its surface area:
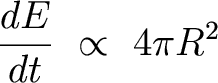
So the cooling rate is proportional to the planets radius:
The center of mass of the moon is not at the moon's geometric center! The center of mass is actually about 2 km closer to the Earth than the geometric center.Why might that be?
So the near side crust is thinner; molten material
(in
the early history of the Moon) could more easily reach the surface to
form
lava basins.