Seismology
Using earthquakes to probe the Earth
Using seismographs placed around the Earth, we can measure
the vibrations due to earthquakes. Earthquakes send waves of various types
through the Earth:
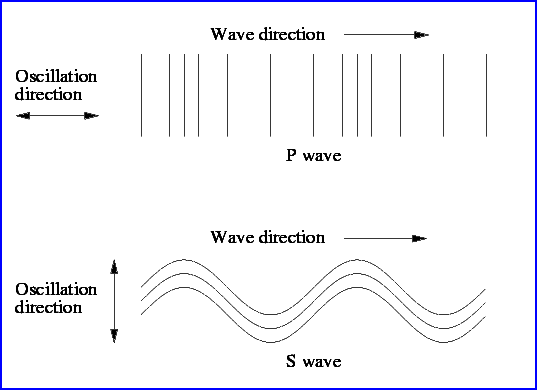
-
P waves (primary or pressure)
- travel through Earth
-
S waves (secondary, or
shear) - also travel through Earth
-
Surface waves - travel
along the surface (provide no information on interior)
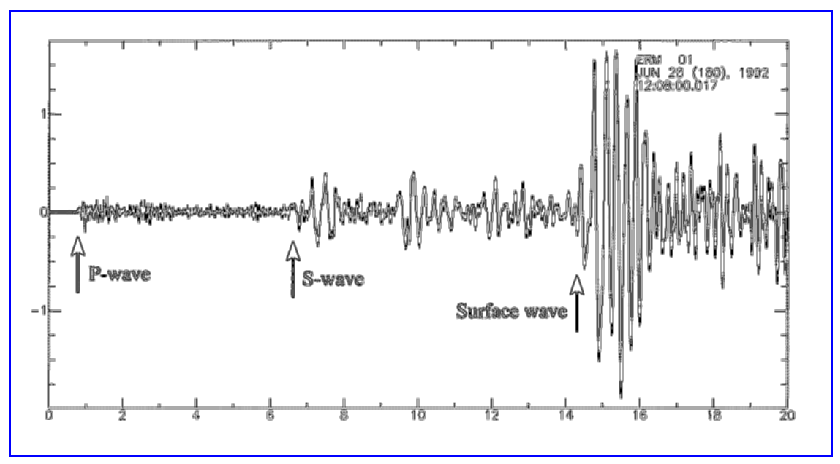
A seismogram:
 How can we use these to probe
the Earth?
How can we use these to probe
the Earth?
-
P waves pass through liquid and
solid, but their speed and direction depend on density changes (refraction).
-
S waves have a different
dependance on density, and cannot travel through liquid.
Use these properties to "map
out" the interior of the Earth:
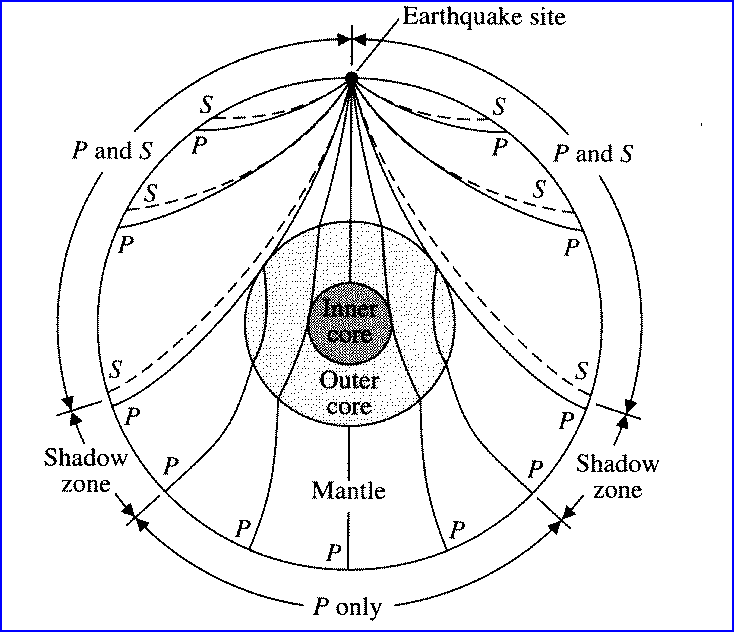 For example:
For example:
-
No S waves on the opposite side of the Earth --> Liquid
Core!
-
Size of the shadow zones give size of the core
-
Travel time differences map out density structure inside
Earth
-
Shadow zones map out layer interfaces



