The luminosity profile of disk galaxies luminosity follows a power law:
L~e-r/h
where h is known as the "scale radius", the distance at which the density drops by 1/e.
|
More recently several authors have argued that at a certain radius, the scale length decreases, causing the profile to falls off much more steeply and effectively truncating the disk. Truncation radii have implications for:
- Interpreting observed galaxy rotation curves
- Formation and evolution of galactic warps
- Galaxy formation
|
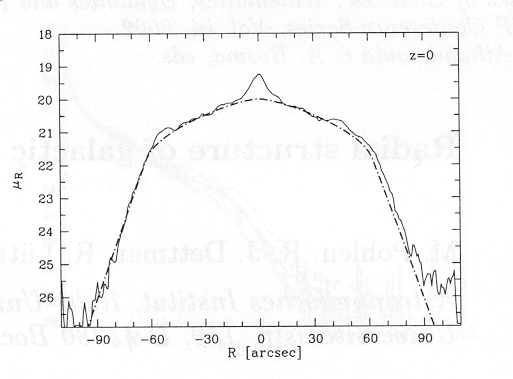
(Pohlen et. al. 2002)
|
Since tidal tails have a strong dependence on the outer edges of the disk, studying tidal tails may give us information about the truncation radii of galaxies.
A starting point: NGC 7252 model
